Monday, May 27, 2019
React image upload or file upload with preview
Today we are going to learn how to upload the file or image in react. Image upload or file upload is a common requirement of the application.
Before start learning file upload We need a `React Project`. If you don't know how to create a new project. Follow this tutorial.
So, Let's get started
Create template
To upload file we need a html template. In this template we will create `file input` element that allows to us to choose the file and a button to upload file. To create it open the `App.js` file and update the render function with the below code.
render() {
let $imagePreview = (<div className="previewText image-container">Please select an Image for Preview</div>);
if (this.state.imagePreviewUrl) {
$imagePreview = (<div className="image-container" ><img src={this.state.imagePreviewUrl} alt="icon" width="200" /> </div>);
}
return (
<div className="App">
<input type="file" name="avatar" onChange={this.fileChangedHandler} />
<button type="button" onClick={this.submit} > Upload </button>
{ $imagePreview }
</div>
);
}
You may notic that we have two method in this `HTML` Fist `fileChangedHandler` and second `submit`
Let's write `fileChangedHandler` function
fileChangedHandler = event => {
this.setState({
selectedFile: event.target.files[0]
})
let reader = new FileReader();
reader.onloadend = () => {
this.setState({
imagePreviewUrl: reader.result
});
}
reader.readAsDataURL(event.target.files[0])
}
The `fileChangedHandler` method will called when the user choose file. It will get the file object of selected file and store in the `selectedFile` state.
Now we will write another function which is responsible to upload the file into the server.
submit = () => {
var fd = new FormData();
fd.append('file', this.state.selectedFile);
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState === 4 && this.status === 200) {
alert('Uploaded!');
}
};
request.open("POST", "https://us-central1-tutorial-e6ea7.cloudfunctions.net/fileUpload", true);
request.send(fd);
}
In this function first we create a new object of the `FormData` and then append the file. then send the request to the server
Here we have crated a `formData` object. We will store the file object to the `formData` and then upload it to the server.
After the all changes our file will looks like this
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
class App extends Component {
state = {
selectedFile: null,
imagePreviewUrl: null
};
fileChangedHandler = event => {
this.setState({
selectedFile: event.target.files[0]
})
let reader = new FileReader();
reader.onloadend = () => {
this.setState({
imagePreviewUrl: reader.result
});
}
reader.readAsDataURL(event.target.files[0])
}
submit = () => {
var fd = new FormData();
fd.append('file', this.state.selectedFile);
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState === 4 && this.status === 200) {
alert('Uploaded!');
}
};
request.open("POST", "https://us-central1-tutorial-e6ea7.cloudfunctions.net/fileUpload", true);
request.send(fd);
}
render() {
let $imagePreview = (<div className="previewText image-container">Please select an Image for Preview</div>);
if (this.state.imagePreviewUrl) {
$imagePreview = (<div className="image-container" ><img src={this.state.imagePreviewUrl} alt="icon" width="200" /> </div>);
}
return (
<div className="App">
<input type="file" name="avatar" onChange={this.fileChangedHandler} />
<button type="button" onClick={this.submit} > Upload </button>
{ $imagePreview }
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
Our application preview
If you loved the tutorial, Please share and if you have any question please comment
Sunday, May 19, 2019
New Angular 7 Upload File or Upload Image with Example
In this tutorial we will learn
file Upload and File progress. Image upload or file upload is a common requirement of the application.Before start learning file upload, We need a
Angular 7 Project. If you don't know how to create a new project. Follow Angular 7 installation guide tutorial.So let's get started
Create template
First we need to create template. In this template we will create
file input element that allows to us to choose the file and a button to submit the form. To create it open the app.component.html file and put the below html on it. Instead of app.component.html you can put on another component too!<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 offset-md-3">
<h3>Choose File</h3>
<form (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<div class="form-group">
<input type="file" name="image" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<button class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Configure the HttpClientModule
We will use the Angular 7
HttpClient to upload the file on the server.
So before writing file upload code, first, Open
src/app/app.module.ts then add this import.import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
Add
HttpClientModule to imports array under @NgModuleimports: [
HttpClientModule
]
Now open the
app.component.ts file and put the below code on itfileData: File = null;
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
fileProgress(fileInput: any) {
this.fileData = <File>fileInput.target.files[0];
}
onSubmit() {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', this.fileData);
this.http.post('url/to/your/api', formData)
.subscribe(res => {
console.log(res);
alert('SUCCESS !!');
})
}
Here you can see the two methods
onSubmit and fileProgress. The fileProgress method will called when the user choose file. It will get the file object of selected file and store in the fileData.
The
onSubmit function will called when the form submit. Here we have created a formData object. We will store the file object to the formData and then upload it to the server via Angular 7 HttpClient
After the changes our
app.component.ts file will looks like thisimport { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'helloworld';
fileData = null;
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
ngOnInit() {
}
fileProgress(fileInput: any) {
this.fileData = <File>fileInput.target.files[0];
}
onSubmit() {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', this.fileData);
this.http.post('url/to/your/api', formData)
.subscribe(res => {
console.log(res);
alert('SUCCESS !!');
})
}
}
Now you can upload the file, But in some case you need more control
Progress Event
If you are dealing with the big file or You may want to show progress to user,
Angular 7 httpClient gives you the progress status.
First of all open the
app.component.ts file and put the below importimport { HttpClient, HttpEventType } from '@angular/common/http';
Then you just need to add
reportProgress to true and set the observe to events in the config like we have below. You will get all the events on subscribethis.http.post('url/to/your/api', formData, {
reportProgress: true,
observe: 'events'
})
.subscribe(events => {
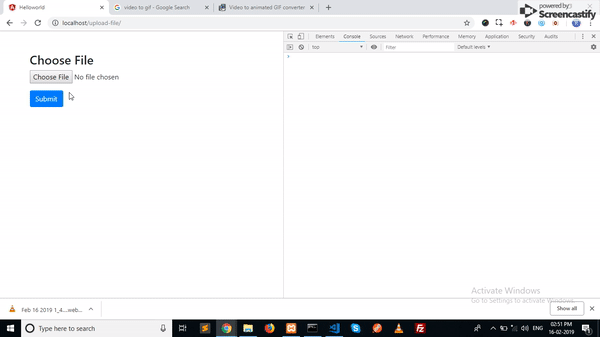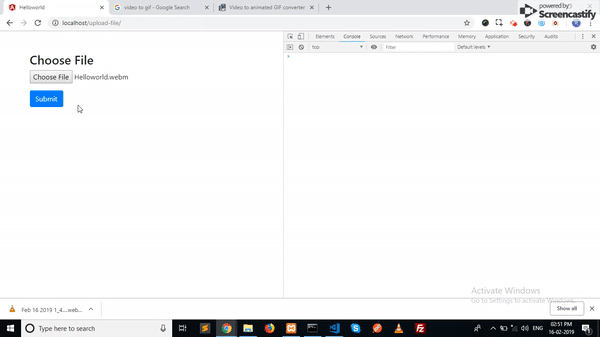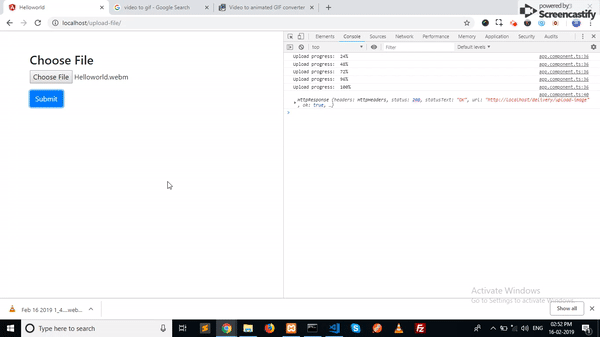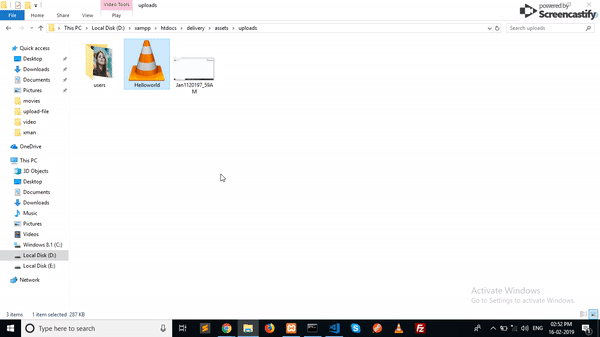
if(events.type == HttpEventType.UploadProgress) {
console.log('Upload progress: ', Math.round(events.loaded / events.total * 100) + '%');
} else if(events.type === HttpEventType.Response) {
console.log(events);
}
})
Here is the how this looks like
Saturday, March 16, 2019
Create and Uses of Laravel Macro with Example
Macro is the powerful feature of the laravel framework.
Macros allow you to add on custom functionality to internal Laravel
components. This laravel macro also work with laravel 5.8 , 5.7 and 5.6 .Let's see Laravel Macro
Example 1
Let's say you are working with the api and want the below response on success
{
"success": true,
"msg": "Your message",
"data": []
}
To achieve the above response. Open the
AppServiceProvider.php file and put the below codeRequest::macro(‘success’, function ($msg, $data) {
Request::json([
"success" => true,
"msg" => $msg,
"data" => $data
]);
});And then use the above defined method
Request::success('Your message', Array());
Example 2
Let's see another example. Suppose you want to create a new method which we will use at the time of fail
Open the
AppServiceProvider.php file and put the below codeRequest::macro(‘fail’, function ($msg, $data) {
Request::json([
"success" => false,
"msg" => $msg,
]);
});
Request::fail('Your message');
Will return
{
"success": false,
"msg": "Your message"
}
You can create another
macro according to your requirement using laravel macroWhich components are “Macroable”?
Macros can be defined on any class with the
Facades
Macroable trait. Below is a list of Macroable facades & classes:Facades
- Cache
- File
- Lang
- Request
- Response
- Route
- URL
- Illuminate\Routing\UrlGenerator
- Illuminate\Cache\Repository
- Illuminate\Validation\Rule
- Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Event
- Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder
- Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relation
- Illuminate\Database\Query\Builder
- Illuminate\Filesystem\Filesystem
- Illuminate\Foundation\Testing\TestResponse
- Illuminate\Http\RedirectResponse
- Illuminate\Http\Request
- Illuminate\Http\UploadedFile
- Illuminate\Routing\ResponseFactory
- Illuminate\Routing\Router
- Illuminate\Support\Str
- Illuminate\Support\Arr
- Illuminate\Translation\Translator
- Illuminate\Support\Collection
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)